
3D Printing in Nigerian Architecture: Opportunities and Challenges
3D Printing in Nigerian Architecture: Opportunities and Challenges
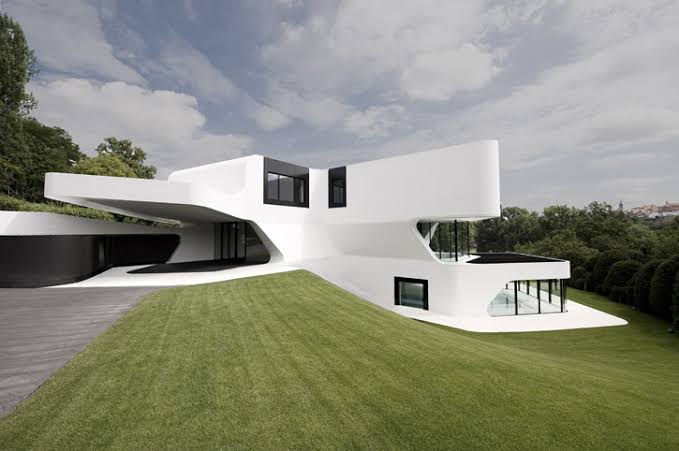
The adoption of 3D printing technology in architecture has the potential to revolutionize construction methods globally. In Nigeria, where the demand for affordable and sustainable housing is rising, 3D printing presents unique opportunities and challenges. This article explores how 3D printing can impact Nigerian architecture, focusing on the prospects and obstacles that accompany this innovative technology.
Opportunities of 3D Printing in Nigerian Architecture
Affordable Housing Solutions

Nigeria faces a significant housing deficit, with millions of citizens living in substandard conditions or lacking access to proper housing altogether. The affordability of 3D printing could address this issue by reducing construction costs. Unlike traditional construction methods, 3D printing requires fewer materials and less manual labor, which significantly cuts down expenses. This cost reduction could make housing more accessible to low-income families and contribute to closing the housing gap.
Speed of Construction

One of the most notable advantages of 3D printing in construction is its ability to speed up the building process. Traditional construction methods can take months or even years to complete a structure, whereas 3D printing can produce a house in a matter of days. In a country like Nigeria, where rapid urbanization is creating an urgent need for quick and efficient construction methods, 3D printing could be a game-changer.
Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
3D printing allows for precise control over the amount of material used in construction, which minimizes waste. Given the environmental challenges associated with conventional building methods, such as high energy consumption and significant material wastage, 3D printing offers a more sustainable alternative. In Nigeria, where resource scarcity and environmental degradation are growing concerns, the use of 3D printing could help promote more sustainable building practices.
Customization and Flexibility in Design
With 3D printing, architects and builders have the flexibility to create complex and customized designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This flexibility can encourage more innovative architectural styles and cultural expressions, allowing for buildings that are more in tune with Nigeria’s diverse cultural heritage and aesthetic preferences. The ability to customize designs easily can also cater to the specific needs of different communities, enhancing the relevance and functionality of new structures.
Job Creation and Skill Development

The introduction of 3D printing in the construction industry has the potential to create new job opportunities and spur skill development in Nigeria. As this technology requires new sets of skills, from operating 3D printers to designing digital blueprints, there will be a demand for training and education in these areas. This could lead to the growth of new educational programs and industries, fostering a skilled workforce and driving economic growth.
Challenges of 3D Printing in Nigerian Architecture
High Initial Investment Costs
Despite the potential cost savings in the long run, the initial investment required for 3D printing technology can be prohibitive. The cost of purchasing and setting up 3D printers, along with the expense of importing materials not locally available, may be too high for many construction firms in Nigeria, particularly smaller enterprises. This financial barrier could slow the adoption of 3D printing in the country.
Lack of Infrastructure and Technical Expertise

For 3D printing to be effectively implemented, adequate infrastructure and technical expertise are essential. In Nigeria, the lack of stable electricity, reliable internet connectivity, and well-maintained roads can pose significant challenges to the widespread use of 3D printing technology. Additionally, there is a shortage of trained professionals who have the expertise to operate 3D printers and develop suitable building materials, which could hinder the growth of this technology in the architecture sector.
Material Limitations

Currently, most 3D printing technologies rely on specific materials, such as concrete and certain plastics, which may not be readily available or suitable for all types of construction in Nigeria. The country’s diverse climate conditions require building materials that can withstand various weather patterns. Therefore, developing locally sourced and climate-appropriate materials for 3D printing will be crucial to the technology’s success in Nigeria.
Regulatory and Standardization Issues
The introduction of new technology in the construction industry often requires updates to existing regulations and standards. In Nigeria, there may be a lack of regulatory frameworks and standards to guide the use of 3D printing in construction. This regulatory uncertainty can create risks for builders and developers, potentially deterring them from adopting the technology.
Resistance to Change
As with any technological advancement, there can be resistance to change, especially in industries that have been traditionally slow to adapt. In Nigeria, where many builders and architects are accustomed to conventional construction methods, there may be a reluctance to embrace 3D printing. Overcoming this resistance will require education, demonstration of the technology’s benefits, and incentives to encourage early adopters.
3D printing holds significant promise for transforming Nigerian architecture by offering affordable, sustainable, and innovative construction solutions. However, the successful adoption of this technology depends on overcoming several challenges, including high initial costs, lack of infrastructure, material limitations, regulatory issues, and resistance to change. By addressing these challenges, Nigeria can unlock the full potential of 3D printing, paving the way for a new era in its architectural landscape. The key will be a strategic approach that balances innovation with practical considerations, ensuring that 3D printing becomes a viable and sustainable option for Nigerian construction.
